IF:9.8 / Associate Professor Xiaopu Ren: Dual-action mechanism of Tamarix polyphenols in inhibiting IQ and MeIQ: Synergistic scavenging of free radicals and trapping of reactive carbonyls
Professors Ren Xiaopu and Li Mingyang from the School of Life and Environmental Sciences at Huangshan University have published a research paper entitled Dual-action mechanism of Tamarix polyphenols in inhibiting IQ and MeIQ: Synergistic scavenging of free radicals and trapping of reactive carbonyls in Food Chemistry, a top-tier journal in the field of engineering and technology (CAS Q1, IF=9.8). Huangshan University is listed as the first affiliation, with Professor Ren Xiaopu serving as the first author and corresponding author. This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32260603), the Key Project for Cultivating Outstanding Young Teachers in Universities of Anhui Province (Grant No. YQZD2024042), and the Scientific Research Start-up Fund of Huangshan University (Grant No. 2024xkjq016).
Highlights:
Tamarix polyphenols suppress 65.97 % IQ in roasted lamb and 83.98 % MeIQ in models.
Dual-action mechanism of Tamarix polyphenols on IQ and MeIQ revealed
Hispidulin excels in radical scavenging and isorhamnetin traps carbonyls
Eight Tamarix polyphenol‑carbonyl adducts identified via UPLC-MS/MS
Synergistic inhibition validated by linear regression
Abstract:Tamarix lamb skewers are highly favored for its distinctive flavor profile, with polyphenol-rich Tamarix branches demonstrating inhibitory effects on heterocyclic amine (HAs) formation during lamb roasting. Four major polyphenols were evaluated for suppressing 2-amino-3-methyl-imidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (IQ) and 2-amino-3,4-dimethyl-imidazo[4,5-f]quinoline (MeIQ) in chemical models and lamb patties. Mechanistic investigations employed Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) to quantify radical scavenging capacity and UPLC-MS/MS to assess reactive carbonyl (acrolein/crotonaldehyde) trapping efficiency. Quercetin showed peak inhibition of 65.97 % (IQ in patties) and 83.98 % (MeIQ in models). Hispidulin exhibited superior radical scavenging (over 90 % reduction at level3), while isorhamnetin displayed optimal carbonyl-trapping performance at level3, and a total of eight distinct mono- and di-adducts structurally were characterized. Linear regression analysis confirmed synergistic inhibition mechanisms via free radical scavenging and reactive carbonyl trapping. This study proposes a dual-action mechanism for natural HAs mitigation, advancing strategies to reduce thermal-processed food hazards.
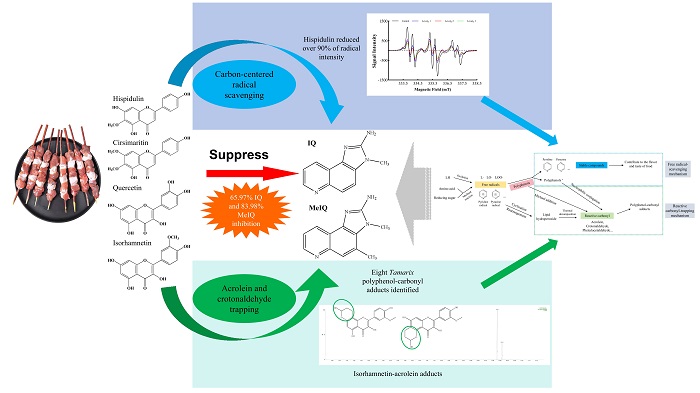
Fig. 1 Proposed dual-action mechanism for polyphenols inhibiting Has
Conclusion:The formation of IQ and MeIQ involves complex chemical pathways, particularly in meat matrix systems, where carbon-centered radicals and reactive carbonyl species (acrolein/crotonaldehyde) jointly contribute to the HAs generation. Effective mitigation strategies should prioritize reducing these precursors during thermal processing. This study established that Tamarix polyphenols suppressed IQ and MeIQ formation through dual mechanisms: scavenging carbon-centered radicals and trapping reactive carbonyls via adduct formation. Eight poly-phenol‑carbonyl adducts were preliminarily characterized, including mono- and di-acrolein conjugates of isorhamnetin and quercetin, mono- acrolein adducts of hispidulin, and mono-crotonaldehyde adducts of isorhamnetin, hispidulin, and quercetin. These findings propose a novel dual-action mechanism: simultaneous radical scavenging and carbonyl trapping disrupt critical precursor pathways, providing new insights for polyphenol-mediated inhibition of heat-induced food hazards.